reading-notes
Read 04 in 201
From the Duckett HTML book:
- Chapter 4: Ch.4 “Links”
- Links are the defining feature of the web because they allow you to move from one web page to another enabling the very idea of browsing or surfing.
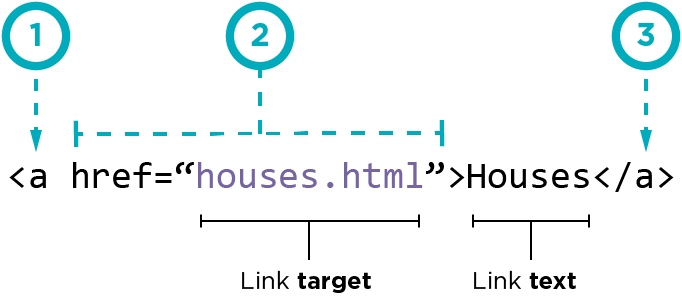
- Links are created using the element. Users can click on anything between the opening tag and the closing tag. You specify which page you want to link to using the href attribute.
- Linking to other sites : we use the AbsoLute urLs
- Linking to other Pages on the same site:we use the relative URL
- On larger websites it’s a good idea to organize your code by placing the pages for each different section of the site into a new folder. Folders on a website are sometimes referred to as directories.
- we can Linking to a speciFic Part oF the same Page.

- we can Linking to a speciFic Part oF Another Page.
- Chapter 15: “Layout”
- CSS treats each HTML element as if it is in its own box. This box will either be a block-level box or an inline box.
- If one block-level element sits inside another block-level element then the outer box is known as the containing or parent element.
- CSS has the following positioning schemes that allow you to control the layout of a page: normal flow, relative positioning, and absolute positioning. You specify the positioning scheme using the position property in CSS. You can also float elements using the float property.
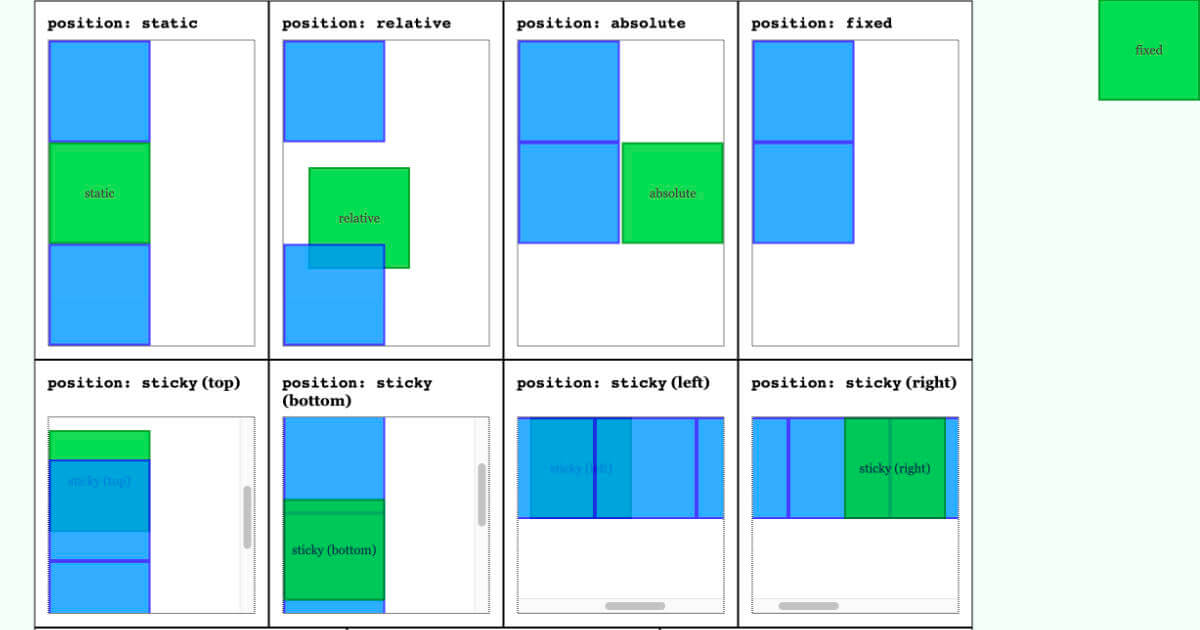
- fixed Positioning This is a form of absolute positioning that positions the element in relation to the browser window, as opposed to the containing element. Elements with fixed positioning do not affect the position of surrounding elements and they do not move when the user scrolls up or down the page.
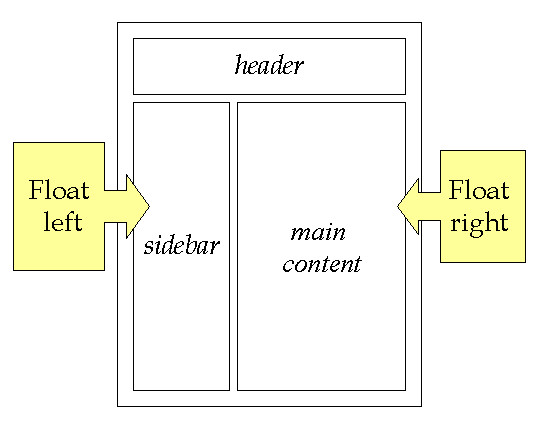
- floating elements Floating an element allows you to take that element out of normal flow and position it to the far left or right of a containing box. The floated element becomes a block-level element around which other content can flow.
From the Duckett JS book:
Chapter 3 (first part): “Functions, Methods, and Objects”
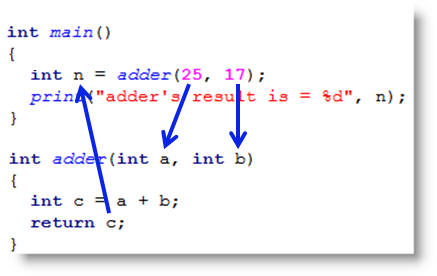
- Functions let you group a series of statements together to perform a specific task. If different parts of a script repeat the same task, you can reuse the function (rather than repeating the same set of statements).
- To create a function , we give it a name and then write the statments needed to achieve it’s task inside the curly braces.(declaration)
- calling faunction : execute all of the statements between it’s curly braces with just one line of code.
- There is function need an informations.

- we can get single or multiple values out of a function.
- some functions have a return statement.